Vietnam: A Textile-to-Garment Giant
Exploring the “Downstream” Powerhouse and its “Upstream” Bottlenecks
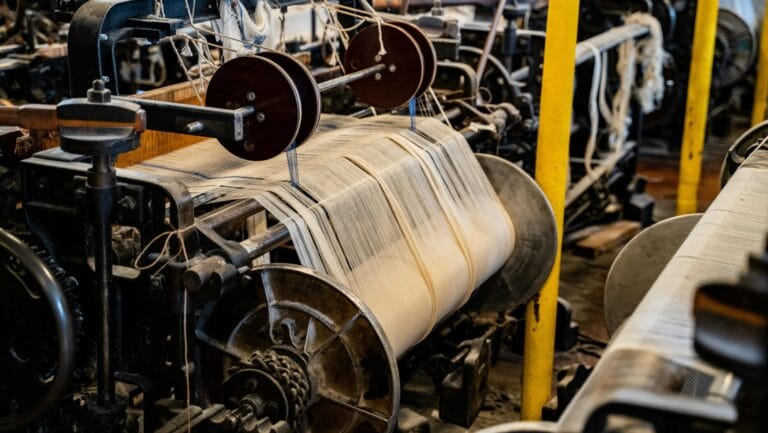
A Global Leader in Garment Assembly
Vietnam is one of the world's largest and most important hubs for garment manufacturing, ranking as the second or third-largest textile and apparel exporter globally. The "Made in Vietnam" tag is ubiquitous on products from major international brands like Nike, Adidas, Zara, and Uniqlo.
A dominant force in textile and apparel exports.
The vast majority operate in "downstream" garment assembly.
The Import Dependency: A Tale of Two Bottlenecks
Despite its assembly strength, Vietnam's industry is characterized by a significant imbalance: it remains heavily underdeveloped in the "upstream" (fiber) and "midstream" (fabric) stages, forcing a massive reliance on imports.
Stage 1: Upstream Raw Materials
The process begins with raw fibers, which are almost entirely imported. This is Vietnam's most significant weakness.
Cotton
Synthetic Fibers
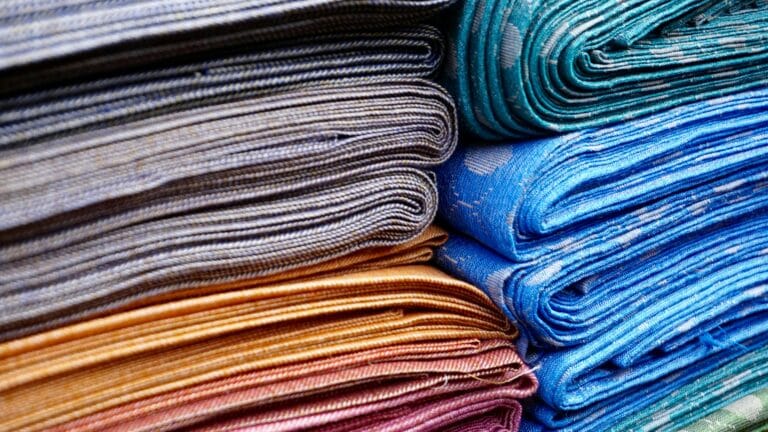
Stage 2: Midstream Fabric Production
This is the "Missing Link." A lack of robust domestic spinning, weaving, and especially dyeing & finishing industries means Vietnam must import the vast majority of its finished fabric.
The Four-Stage Process Flow
This is the end-to-end flow, highlighting where Vietnam's industry fits into the global picture. The process is dominated by imports at the start and exports at the end.
Upstream: Sourcing
Begins with raw fibers, which are almost entirely imported from suppliers in China, South Korea, India, and the US.
BOTTLENECK
Midstream: Fabric
Fibers are spun, woven/knitted, and dyed. Vietnam imports 65-70% of finished fabric to bypass this weak domestic link.
BOTTLENECK
Downstream: Assembly
Vietnam's core strength. Factories use the imported fabric to Cut, Make, and Trim (CMT) garments for global brands.
CORE STRENGTH
Post-Production: Export
Finished, packed garments are shipped to key markets, primarily the United States, Europe, Japan, and South Korea.
FINAL OUTPUT
Inside the "Cut-Make-Trim" (CMT) Model
This is the assembly process that defines Vietnam's role. The factory is provided with all materials and a "tech pack" (design blueprint) and is paid for the service of assembly.
Pre-Production
Receive tech pack and materials; create approval samples.
Fabric Inspection
Imported fabric rolls are checked for any flaws.
Cutting (The "C")
Fabric is laid out and cut into precise pattern pieces.
Sewing (The "M")
Cut pieces are moved to assembly lines and stitched together.
Finishing (The "T")
Threads are trimmed; buttons, labels, and zippers are attached.
Quality Control (QC)
Final garments are inspected for measurements and defects.
Moving Up the Value Chain
The future of Vietnam's industry depends on moving beyond the low-profit CMT model to capture more value. This chart shows the approximate breakdown of current production models, with a strong shift towards higher-value FOB/OEM.
Data Sources
This infographic is a synthesis of data from industry reports and publications, including:
Related Posts
 15 Common Tech Pack Mistakes &… 22 Oct 2025
15 Common Tech Pack Mistakes &… 22 Oct 2025 Garment Defect Inspection Sheet Template 10 Oct 2025
Garment Defect Inspection Sheet Template 10 Oct 2025 Behind the Seams: A Practical Guide… 09 Oct 2025
Behind the Seams: A Practical Guide… 09 Oct 2025